Web Application Security: Best Practices, Testing, and Assessment for 2025
Web application security is a practice to protect web applications or online services from cyber attacks that aim to steal data, damage the operations or compromise users

Web Application Security: Best Practices, Testing, and Assessment for 2025
Web application security is essential to protect your apps from cyberattacks that target sensitive data and disrupt operations. This guide covers the importance of web app security, common vulnerabilities, best practices, and testing methods, helping you secure your application, ensure compliance, and maintain user trust
Summary
-
What is Web Application Security?
Web application security protects online apps from data theft, unauthorized access, and service disruption caused by cyberattacks. -
Why Web Application Security Matters
Modern web apps handle sensitive data—any vulnerability can lead to breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage. -
Common Web Application Security Issues
From SQL injection to misconfiguration, understanding common vulnerabilities is the first step to building a secure app. -
Web Application Security Best Practices
Following secure coding, encryption, and least privilege access principles helps reduce your attack surface effectively. -
Web Application Security Testing
Testing approaches like SAST, DAST, and IAST detect vulnerabilities early, ensuring safer releases. -
Web Application Security Audit
Audits provide a structured review of your security posture, helping you comply with frameworks like GDPR or HIPAA. -
How to Check Web Application Security
Automated scans, penetration tests, and platforms like Plexicus streamline vulnerability detection and remediation. -
FAQ: Web Application Security
Explore key questions around testing, auditing, and best practices for web application protection.
What is Application Security ?
Web application security is a practice to protect web applications or online services from cyber attacks that aim to steal data, damage the operations or compromise users.
Today, applications are heavily in web apps, from e-commerce to SaaS dashboards. Protecting web applications from cyber threats has become essential to protecting customers’ data, organizational data, gaining customer trust, and aligning with compliance regulations.
This article will guide you to explore web application security best practices, testing methods, assessment, audits, and tools to protect your web application against attackers.

Why web application security matters ?
Web applications are often used to store and process various data, from personal information, business transactions, and also payments. If we leave a web application with a vulnerability, it will make attackers:
- steal the data, including personal information, or financial-related information (e.g, credit card number, user login, etc.)
- inject malicious script or malware
- hijack users’ sessions and pretend to be a user of its web application
- Take over the server and launch a large-scale security attack.
Web application attacks are also becoming the top three patterns alongside system intrusion and social engineering across various industries.
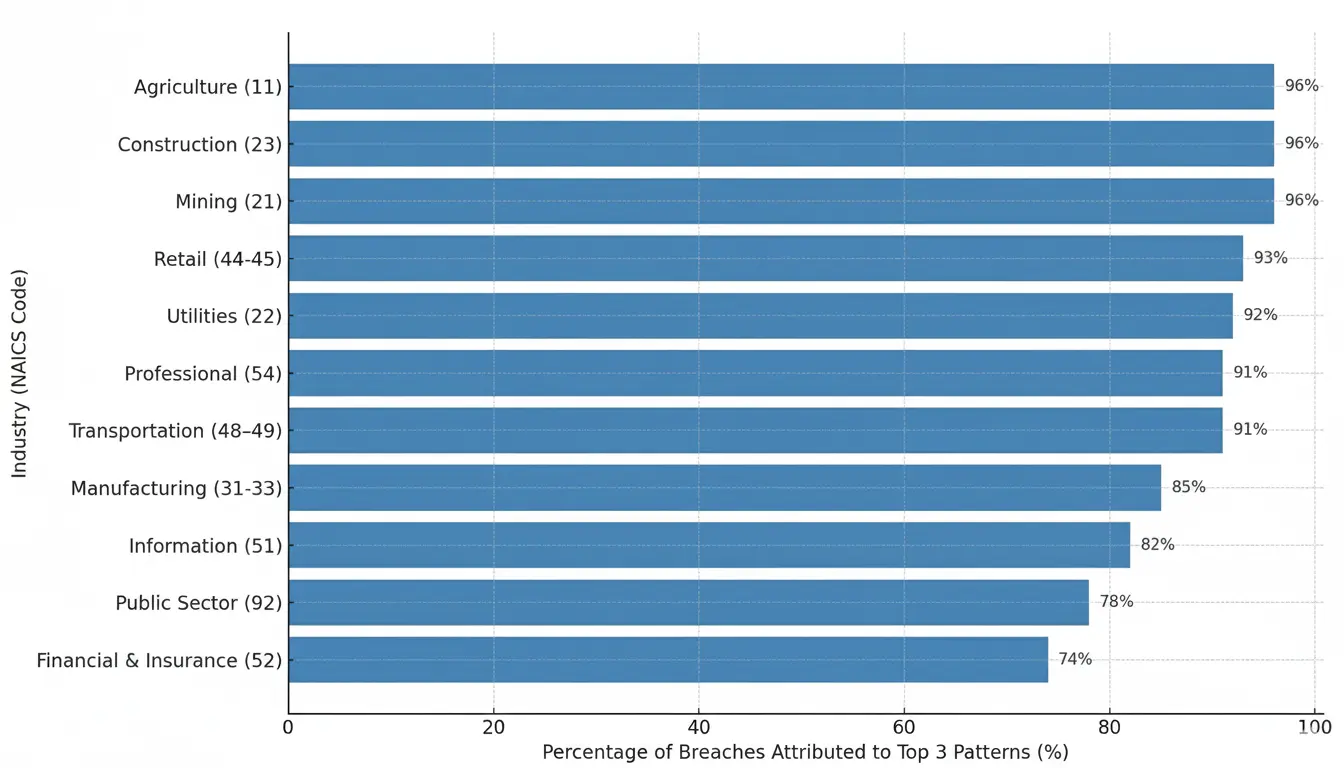
Here’s the bar chart showing the percentage of breaches attributed to the top three patterns (including Basic Web Application Attacks) across different industries (sources : Verizon DBIR - 2025)
| Industry (NAICS) | Top 3 Patterns Represent… |
|---|---|
| Agriculture (11) | 96% of breaches |
| Construction (23) | 96% of breaches |
| Mining (21) | 96% of breaches |
| Retail (44-45) | 93% of breaches |
| Utilities (22) | 92% of breaches |
| Transportation (48–49) | 91% of breaches |
| Professional (54) | 91% of breaches |
| Manufacturing (31-33) | 85% of breaches |
| Information (51) | 82% of breaches |
| Financial and Insurance (52) | 74% of breaches |
If we break down based on global region, it gives us a clearer picture of how web application security is very important to prevent cyber threats .
Below data incident classification patterns (source : Verizon DBIR - 2025)
| Global Region | Top 3 Incident Classification Patterns | Percentage of Breaches Represented by Top 3 Patterns |
|---|---|---|
| Latin America and Caribbean (LAC) | System Intrusion, Social Engineering, and Basic Web Application Attacks | 99% |
| Europe, Middle East, and Africa (EMEA) | System Intrusion, Social Engineering, and Basic Web Application Attacks | 97% |
| Northern America (NA) | System Intrusion, Everything Else, and Social Engineering | 90% |
| Asia and the Pacific (APAC) | System Intrusion, Social Engineering, and Miscellaneous Errors | 89% |
This overview makes the web application security assessment critical to secure the web application from a cyber attack.
Common Web Application Security Issues
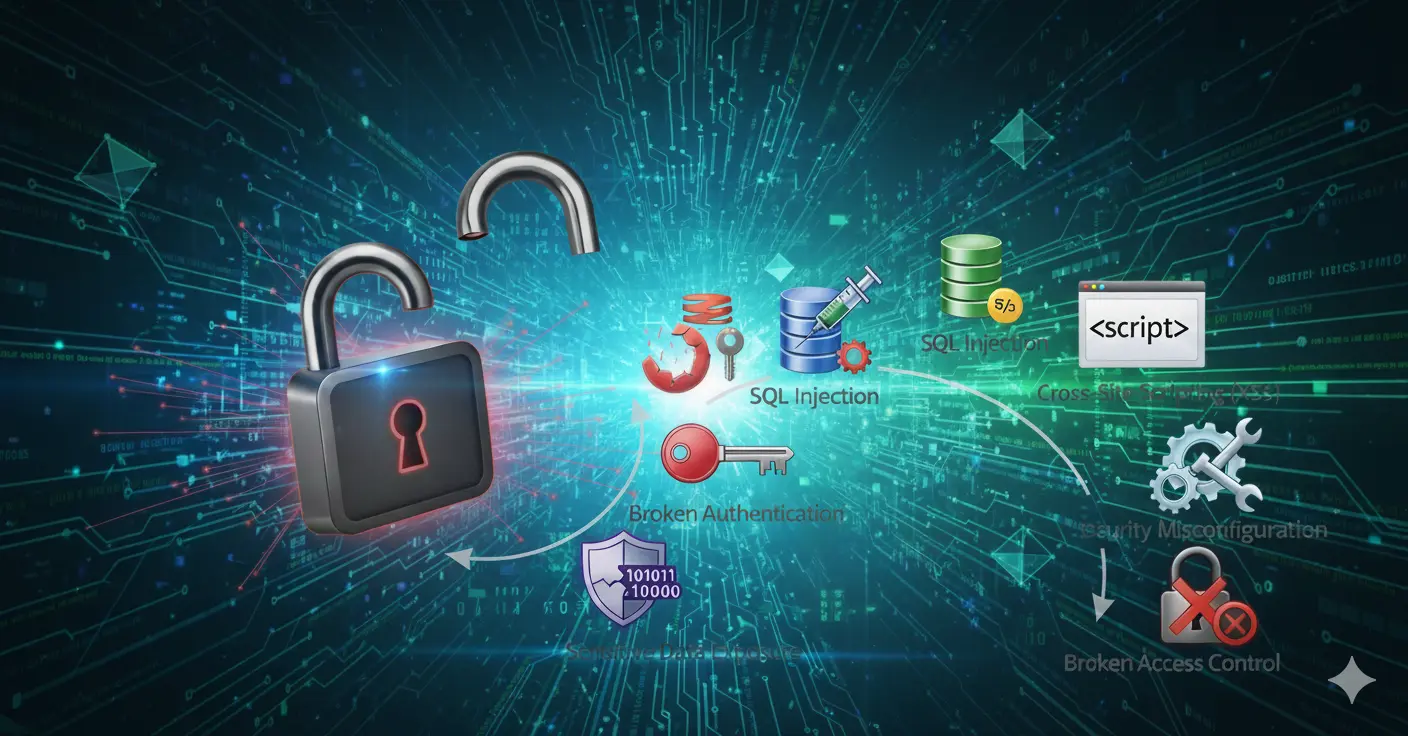

Understanding typical issues is the first step to securing a web application. Below are common web application issues in web applications:
- SQL Injection : attackers manipulate queries to the database to get access or alter the database
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) : execute a malicious script that runs in the user’s browser, which will allow the attacker to steal the user’s data
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) : an attacker’s technique to make a user execute an unwanted action.
- Broken Authentication : weak authentication allows attackers to pretend to be users.
- Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR) : Exposed URLs or IDs that give attackers access to the system
- Security Misconfigurations : Misconfiguration in container, cloud, APIs, server that open the door for attackers to access system
- Insufficient Logging and Monitoring : breaches are undetected without proper visibility
You can also refer to OWASP Top 10 to get updates about the most common security issues in web applications.
Web Application Security Best Practices
Below is the best practice you can use to minimize the security issues in your web application :
- Adopt Secure Coding Standards : Follow the framework and guidelines that align with the secure software development lifecycle (SSDLC)
- Apply Strong Authentication & Authorization : Use strong authentication methods like MFA, role-based access control (RBAC), and session management.
- Encrypt Data: Protect data with encryption either in transit (TLS/SSL) and at rest (AES-256, etc.)
- Conduct Regular Testing & Security Audit : Conduct regular penetration testing or security assessment to discover emerging vulnerability issues.
- Patch and Update Frequently : Keep the framework, server, and libraries up to date to close known vulnerability issues.
- Use Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) : Prevent malicious traffic from coming to your app.
- Secure APIs : Apply security standards to your API endpoints
- Implement Logging & Monitoring : Detect suspicious behaviour with SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) or monitoring tools.
- Apply Least Privilege : Minimize permission for each database, application, services and users. Only give access to what they need.
- Train Developers and Staff : Increase awareness about security by training them to implement security standards in their role.
Web Application Security Testing
Web application security testing is a process to check vulnerabilities in the application to secure the app from attackers. It can be done in multiple stages of development, deployment, and runtime to ensure that vulnerabilities are fixed before being exploited by attackers.
Types of Web Application Security Testing:
- Static application security testing (SAST) : scan source code to find vulnerabilities before deployment
- Dynamic application security testing (DAST) : Simulate a real attack in a running application to uncover vulnerabilities.
- Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST) : combines SAST and DAST to find vulnerabilities, it will analyze the response of every action during testing
- Penetration testing : ethical hackers will make a real test of the application to uncover hidden vulnerabilities that might be missed by automation testing
With Plexicus ASPM, these different testing methods are brought into a single workflow. The platform integrates directly into the CI/CD pipeline, giving developers instant feedback on issues like vulnerable dependencies, hardcoded secrets, or insecure configurations, long before applications go to production.
Web Application Security Testing Checklist
The structured checklist will help you find vulnerabilities more easily. Below checklist you can use to secure your web application :
- Input validation : to avoid SQL Injection, XSS, and injection attacks.
- Authentication mechanisms : enforce MFA and strong password policies
- Session management : ensure session and cookies are secure
- Authorization : Verify that users can only access resources and actions permitted to their roles (no privilege escalation)
- API endpoints : check to avoid exposed sensitive data
- Error handling : avoid displaying system details in error messages
- Logging & monitoring : ensure the system can also track unusual behaviour
- Dependency scanning : look for vulnerabilities in third-party libraries
- Cloud configuration : ensure there is no misconfiguration, verify least privilege, secure keys, and proper IAM roles.
Web Application Security Audit
A web application security audit is different from web application security testing. An audit gives you a format review of your application security program. Meanwhile, the goal of security testing is to find vulnerabilities; the security audit goal is to measure your application against standards, policies, and compliance frameworks.
Application security audit, including :
- security web coding practice
- compliance mapping (e.g, GDPR, HIPAA, etc.)
- third-party dependencies analysis
- effectiveness of monitoring and incident response
A security audit will help your organization to secure the application and meet regulatory standards.
How to Check Web Application Security
Organizations often do the following steps :
- Run automated security scan (SCA, SAST, DAST)
- Perform manual penetration testing.
- Review configuration on the server, container, and cloud infrastructure
- Audit access control and enforce MFA (multi-factor authentication)
- Track remediation with ticketing integration, like Jira or a similar tool
Platforms like Plexicus make vulnerabilities check easier, even more with Plexicus provides AI remediation to help you accelerate in solving security issues.
FAQ: Web Application Security
Q1 : What is web application security?
Web application security is the implementation of protecting web applications from cyber threats.
Q2 : What is web application security testing?
A process to access, scan, and analyze web applications with various security testing methods (SAST, DAST, SCA, etc) to find vulnerabilities before it exploited by attackers.
Q3 : What are web application security best practices?
Practice to implement security approach in web application, including validation, encryption, authentication, and regular patching.
Q4 : What is a web application security audit?
An audit is a formal review of your security application, often used to comply with compliance and regulatory standards.
Q5: What are web application security assessment tools?
These are platforms that scan, test code, dependencies, configuration, runtime, and environment to find vulnerabilities.
Q6 : How to check web application security?
By combining automated scans, penetration tests, audits, and continuous monitoring. Using integrated platforms like Plexicus streamlines this process.


